Last article we covered about key factors that influence project management, please click here to view previous article. In this article, we shall cover about Process Framework, this is heart of PMP exam, understanding this, will help us understand next chapters going forward.
PMP Process framework is composed of Input, Tools and Techniques and Output.
A project management process takes a list of inputs and converts to specific output with use of tools and techniques. Every process of 49 different Processes is unique and performed to resolve a specific problem in the project. Please refer my earlier article on Processes, Knowledge area and Process groups.
Inputs : could be specific information or artifact, which may also be an output of some other process.
Tools and Techniques: are methods and practices to convert the inputs to outputs.
Outputs: could be documents, information, result or a product and this output of one process can be an input to other process.
Common Inputs: below are set of common inputs to each process, this will help us remember process inputs easily, this is been covered in previous article, influence on project management. Here, I am listing for the reference.
- Enterprise Environmental Factors
- Organizational Process assets
- Project Management Plan
- Work performance data
- Work performance Information.
Hope this information helps! Next we shall focus on each process groups one by one.
————————————–
for queries, suggestions, feedback contact on
email :bipinparshottam@gmail.com
skype: bipin.pankhania


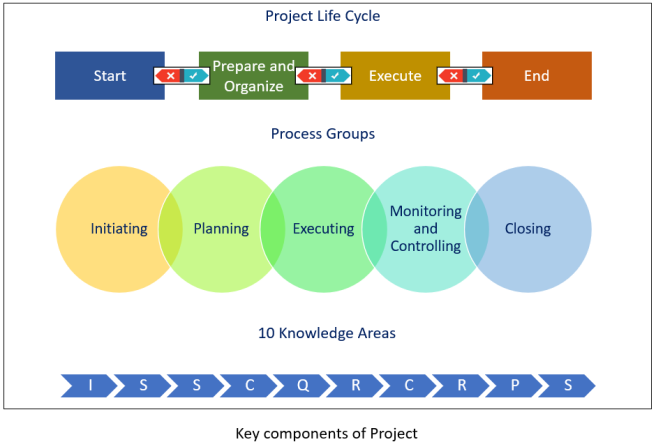 Project Phases: a collections of logically related activities that produces one or more deliverable. In above image Start, Prepare and Organize, Execute and End is the project phases.
Project Phases: a collections of logically related activities that produces one or more deliverable. In above image Start, Prepare and Organize, Execute and End is the project phases.